Water Harvesting in Urban Areas: Strategies, Benefits, and Challenges
Urban water harvesting encompasses a suite of techniques aimed at capturing, storing, and utilizing rainwater and stormwater within city environments. This approach addresses critical issues such as water scarcity, urban flooding, and environmental degradation, offering a sustainable solution to urban water management.
Techniques for Urban Water Harvesting
Rainwater Harvesting Systems
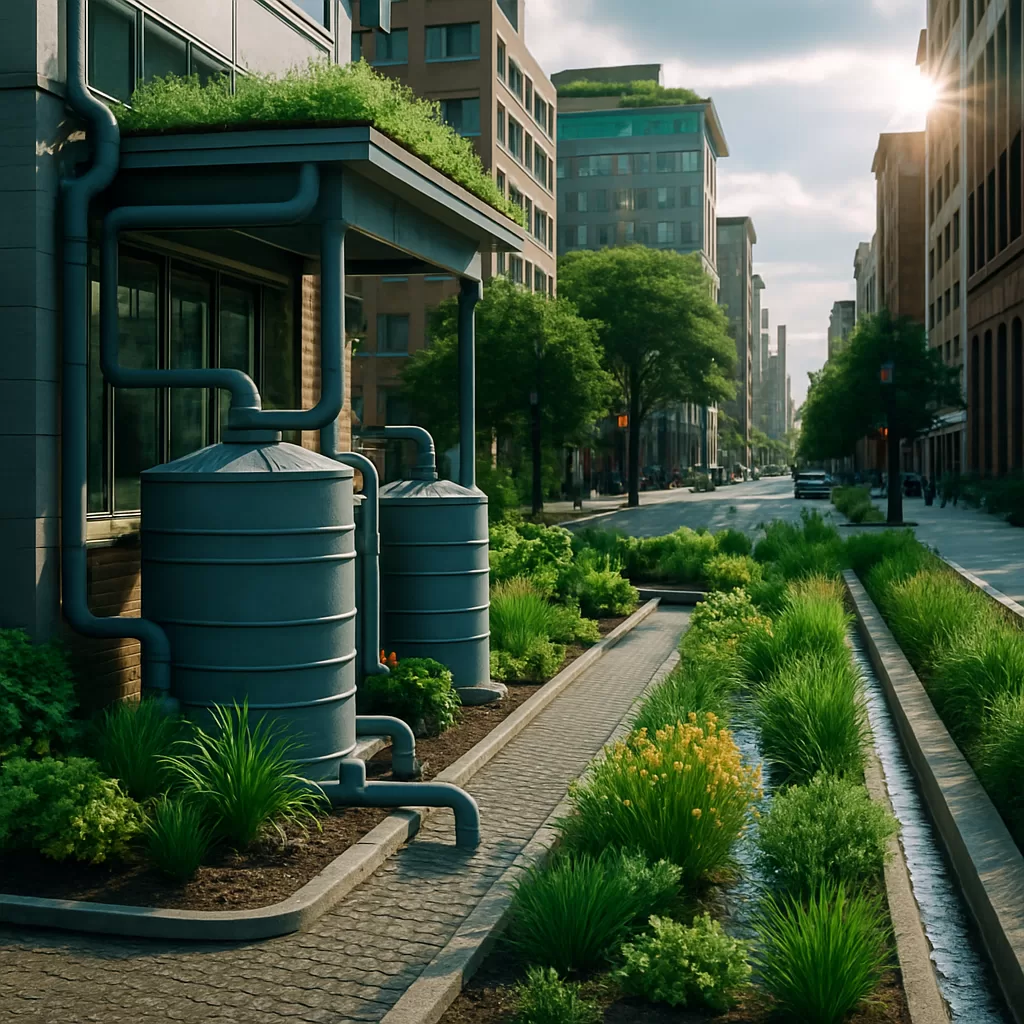
Rainwater harvesting involves collecting and storing rainwater from rooftops and other surfaces for later use. Common applications include non-potable uses such as irrigation, toilet flushing, and laundry. In South Africa’s City of Johannesburg, only 0.1% of the population utilizes rainwater harvesting, highlighting the need for broader adoption. ([1])
Stormwater Management Practices
Effective stormwater management reduces runoff and mitigates flooding. Techniques include permeable pavements, which allow water to infiltrate the ground, and rain gardens that capture and filter stormwater. These methods not only manage water flow but also improve water quality by filtering pollutants. ([2])
Green Infrastructure
Green infrastructure integrates natural systems into urban design to manage water sustainably. Examples include green roofs, which absorb rainwater and reduce runoff, and bioswales, vegetated channels that filter and convey stormwater. These practices enhance urban aesthetics and provide ecological benefits. ([3])
Benefits of Urban Water Harvesting
Environmental Benefits
Implementing water harvesting techniques reduces the strain on existing water resources and minimizes urban flooding by decreasing surface runoff. Additionally, practices like rain gardens and permeable pavements promote groundwater recharge, contributing to the sustainability of urban water supplies. ([4])
Economic Benefits
Utilizing harvested rainwater for non-potable purposes can lead to significant cost savings on water bills. For instance, in Jodhpur, India, a housing complex implemented a rainwater harvesting system that captures approximately 21.1 million liters of rainwater annually, reducing dependence on municipal water supply and saving about Rs. 2.36 million each year. ([5])
Social Benefits
Water harvesting initiatives can foster community engagement and education. By involving residents in the design and implementation of these systems, communities can promote environmental awareness and encourage collective efforts toward sustainable water management. ([6])
Challenges in Implementing Urban Water Harvesting
High Initial Costs
The development and maintenance of water harvesting infrastructure can be expensive, requiring significant investment from municipalities and property owners. This financial barrier often hinders widespread adoption. ([7])
Urban Planning Limitations
Retrofitting existing urban areas with water harvesting systems poses logistical and technical challenges. Limited space and existing infrastructure can complicate the integration of new systems. ([8])
Public Awareness and Acceptance
A lack of understanding about the benefits and operation of water harvesting systems can lead to resistance or underutilization. Educational campaigns and community involvement are essential to overcome these challenges. ([9])
Case Studies
Johannesburg, South Africa
In Johannesburg, the adoption of rainwater harvesting is minimal, with only 0.1% of the population utilizing such systems. Challenges include financial viability, reliability, quality concerns, and system maintenance. Policy reforms are suggested to facilitate innovation uptake, stakeholder engagement, and compliance. ([10])
Guangxi, China
A sports center project in Guangxi implemented Low Impact Development (LID) practices as part of the “sponge city” initiative. The project included bio-retention facilities and sunken green spaces, achieving a 75% annual total runoff reduction and enhancing ecological services. ([11])
Urban water harvesting presents a viable solution to address water scarcity, manage stormwater, and promote sustainable urban development. While challenges such as high initial costs and public awareness persist, successful case studies demonstrate the potential benefits. Strategic planning, policy support, and community engagement are crucial for the widespread adoption and success of water harvesting initiatives in urban areas.
Bibliography
[1,10] – https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/1573062X.2019.1637907
[2,7,8,9] – https://aquafitbd.com/blogs/urban-stormwater-harvesting-a-sustainable-solution-for-water-scarcity
[3] – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Green_infrastructure
[4] – https://agriculture.institute/water-harvesting-conservation-utilisation/benefits-rooftop-rainwater-harvesting-urban-areas/
[5] – https://www.researchgate.net/publication/389135319_Urban_Rainwater_Harvesting_-_Case_studies_from_different_agro-climatic_regions
[6] – https://sustainableliving.org.nz/top-benefits-of-rainwater-harvesting-in-urban-areas/
[11] – https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.10347