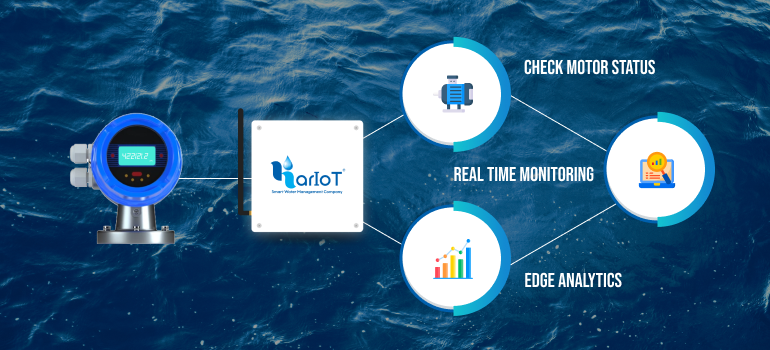
Smart water meters are a transformative technology driving behavioral change for sustainable water use by providing detailed, real-time consumption data that increases user awareness and encourages efficient water habits. These meters oer transparency through continuous feedback, alerting users of excessive use or leaks, which prompts immediate corrective actions and fosters long-term water conservation habits. The ability to set usage goals, benchmark against peers, receive personalized recommendations, and access financial incentives further motivates households and businesses to reduce water wastage. Utility providers benefit from increased accountability, improved operational efficiency, and community wide engagement programs. Despite challenges such as resistance to technology adoption and privacy concerns, smart water meters have demonstrated significant reductions in water consumption and are pivotal for sustainable urban water management.
Awareness and Real-Time Feedback
Smart water meters revolutionize water management by providing users with transparent, detailed, and real-time data about their water consumption patterns. This immediate visibility into usage raises awareness—a critical first step in behavioral change. Studies show that just being aware of one’s water consumption can reduce usage by up to 10%. Feedback loops, including alerts when consumption exceeds predetermined thresholds, create a direct and prompt communication channel that encourages users to consciously adjust their behaviors to conserve water. This heightened transparency also compels water utilities to improve their service quality and responsiveness to customer needs, leading to enhanced trust and cooperation.
Behavioral Motivation Tools
These meters incorporate features such as goal-setting, benchmarking, and gamification, all of which leverage psychological and social influences to promote sustainable water behaviors. Users can set consumption targets and compare their water use to that of other households or businesses, fostering a competitive spirit that encourages conservation. Many smart meter platforms oer apps that allow participation in water-saving challenges, reinforcing positive behavior through rewards or recognition. Additionally, personalized recommendations based on users’ unique consumption patterns empower decision-making, such as detecting leaks or upgrading appliances to water-efficient models, increasing the efficacy of water-saving efforts.
Financial and Community Incentives
Smart water meters enable more accurate billing based on actual consumption, replacing flat-rate or estimated billing that often leads to careless water use. Dynamic pricing models can charge higher rates for excessive use, financially motivating users to reduce their water footprint. Beyond individual incentives, utilities can leverage meter data to implement community-wide water-saving programs, encouraging neighborhoods to collaborate on conservation eorts. Such community engagement creates social norms around water conservation, leading to ripple eects where individuals are influenced by peers’ responsible behaviors, amplifying sustainable water use benefits.
Leak Detection and Operational Efficiency
An important technical benefit of smart water meters is their ability to detect leaks promptly, often unnoticed in traditional systems. Early leak detection prevents significant water loss and encourages timely repairs, protecting the overall water supply. From the utility perspective, smart meters enable enhanced monitoring of non-revenue water and unaccounted-for water, improving water loss management. Automation of meter reading and billing reduces labor needs and human error, streamlining operations and enabling utility staff to focus on more complex tasks. This creates an efficient, transparent water management ecosystem that supports sustainable resource use.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite their potential, smart water meters face hurdles such as user resistance to adopting new technology, lack of motivation to change established habits, and concerns regarding privacy and data security. Ensuring user trust and demonstrating the tangible benefits of smart meters are essential for widespread adoption. Cost remains a barrier, particularly in less a uent areas, where the upfront investment for installation might be prohibitive. Nonetheless, successful initiatives across cities have shown that with proper education, engagement, and support mechanisms, these challenges can be mitigated.
Case Studies and Impact
Empirical research confirms the positive impact of smart water meters on water conservation. For example, implementation in various households has led to water consumption reductions from 5.3% to as high as 27%, depending on the study and technology used. Cities deploying large-scale smart meter programs have documented reduced water wastage by up to 15%, illustrating the significant operational and environmental benefits. By transforming billing systems and empowering consumers with data, these programs promote a culture of sustainability crucial for combating water scarcity and managing future urban water demands.
In summary, smart water meters are powerful enablers of behavioral change, fostering sustainable water use through enhanced awareness, real-time data, personalized feedback, and financial incentives. They not only empower consumers but also enhance utility service efficiency and community engagement. While adoption challenges exist, the demonstrated water savings and efficiency gains position smart water meters as key technology for sustainable urban water management and conservation efforts globally.