E-Waste, as a generic term, describes all types of old, end-of-life or discarded electrical and electronic equipments including all components, sub-assemblies and consumables, which are part of the product at the time of discarding. This form of waste encompasses All the listed items and many others add ease, comfort, and luxury to the modern life and have therefore become an indispensable part of modern societies. However, short lifespan, limited repair options and fast-changing technology is turning a high proportion of electronic gadgets into waste upon the end of its usable…
Read MoreCategory: Case Study
Nanobubble Technology: Transforming the Landscape of Sustainable Water Management
In the face of escalating global water challenges, innovative solutions are critical for ensuring sustainable water management. Nanobubble technology, an emerging advancement in water treatment, is revolutionizing how industries, agriculture, and municipalities address water quality, conservation, and reuse. WHAT IS NANO-BUBBLE? Imagine bubbles so small that they’re nearly invisible to the naked eye — yet powerful enough to transform industries and ecosystems. Welcome to the world of nanobubbles. These ultra-tiny gas bubbles, smaller than 200 nanometers in diameter (about 500 times smaller than a human hair!), are breaking the rules…
Read MoreWater Filtration – An art to protect and enhance life of membranes & human health
Water… water… everywhere but there is no water for drinking! This is a popular sentence for us to understand that every water is not potable. Though plenty of water is available, all the water is not potable. Ground water and surface water are the two major water sources for drinking and other uses. Water may contain large numbers of contaminants which includes physical, chemical and microbiological. Physical contaminants include sand, silt, mud, etc. Chemical contaminants include inorganic chemicals like heavy metals, chlorides, sulphates, iron, nitrates, nitrites etc. and organic chemicals…
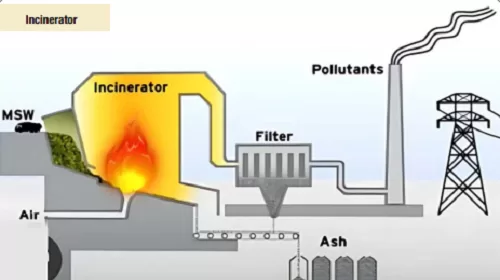
Read MoreOptimized Management of Municipal Solid Waste for Environmental Sustainability: Techniques And Technologies
Municipal solid waste, commonly known as trash or garbage, consists of everyday items discarded by households, businesses, and institutions. By definition, it includes waste from various sources such as domestic wastes, commercial establishments, institutions, industries, and construction. It typically includes the following with varying proportions depending on the location, socioeconomic factors, and consumption patterns of the society: Organic Waste: Food scraps, garden trimmings, and other biodegradable materials. Recyclables: Paper, cardboard, plastics, metals, and glass. Hazardous Waste: Batteries, electronic waste (e-waste), and chemicals. Inert Waste: Construction debris and other non-biodegradable materials.…
Read MoreMott Macdonald Bentley standardizes phosphorous removal schemes, delivering infrastructure and intelligence benefits to the U.K. water industry
ProjectWise Component Center Helps Facilitate Repeatable Workflows to Save More Than GBP 3.7 Million Supporting Environmental Sustainability. Meeting stringent requirements for phosphorous removal The United Kingdom water industry’s Asset Management Plan 7 (AMP 7) includes a heightened priority for improving water quality schemes. In particular, it focused on reducing the amount of phosphorous released into watercourses, which are natural or artificial channels where water flows. Originating from a range of sources, including wastewater discharge and water main leakages, high levels of phosphorous yields extensive algae growth, posing a significant threat…
Read MoreAchieving consistent low energy consumption in sea water RO based desalination plants using Lowatt® technology
Abstract Biofouling remains the single most important factor that increases energy consumption as time progresses in the operation of the Reverse Osmosis (RO) membrane system. One of the challenges with plant operation is that once a plant has been designed for certain energy consumption, it does not remain steady over a period. This is mainly due to biofouling and the inability to clean the membrane efficiently. In an effort to maintain healthy operational efficiency in terms of water production and energy consumption, differential pressure across the membranes should remain constant…
Read MoreQdos CWT chemical metering pump doses chlorine without fail for over 15,000 hours at Ergon INC.
• A Qdos CWT (Conveying Wave Technology™) chemical metering pump is dosing chlorine at Ergon – West Virginia Inc.’s crude oil refinery in Newell • Ergon has switched to Qdos CWT for its reliability and longer life to dose chlorine • Diaphragm pumps lasted eight to ten months on average for Ergon, but the Qdos CWT had a life of more than 21 months (equivalent to 15,000 hours) A Qdos CWT (Conveying Wave Technology™) chemical metering pump ran for over 21 months dosing chlorine at Ergon – West Virginia Inc.’s…
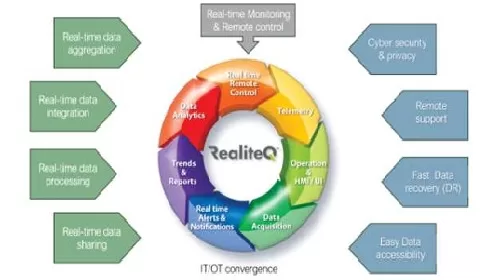
Read MoreDigital transformation in water utility
Background: Many water utilities around the world have been suffering for years from underinvestment, alongside significant deterioration of the water system due to aging infrastructure and inadequate maintenance. Today, water utilities face additional challenges, such as increased water consumption coupled with a decrease in water sources due to extreme climatic events, pollution, and inefficient management of existing systems. Additionally, there is a need to enhance control and monitoring of all water systems to ensure a continuous supply of safe drinking water to the entire population. This challenge is even greater…
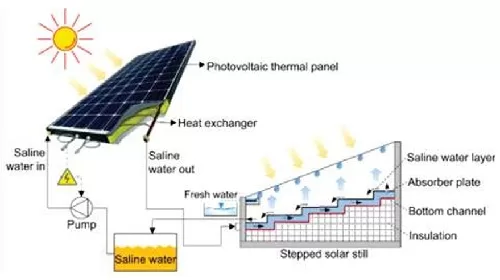
Read MoreRecent technologies for desalination of water
Water is often taken for granted, yet for many around the globe, it is a precious and increasingly scarce resource. As populations grow and climate change disrupts traditional water cycles, the availability of fresh water is becoming a critical concern. The World Health Organization reports that over 2 billion people live in countries experiencing high water stress. In response, the world is turning to the ocean, which covers over 70% of our planet, as a vast and largely untapped source of fresh water through the process of desalination. Desalination, the…
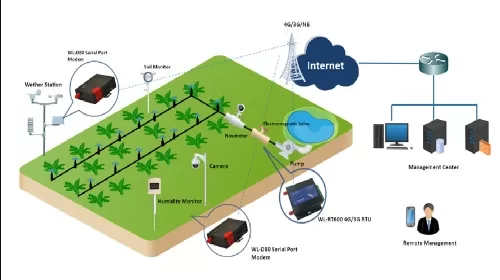
Read MoreUrgency meets innovation: Tech’s role in resolving water crisis
As you leaf through today’s newspaper, the resounding message is crystal clear: we’re facing a dire water crisis, and the urgency to address it is palpable as time ticks away. India grew from merely 51 million tons (Mt) of food grain production in 1950/51 to over 314 Mt in 2022- a sixfold increase in production. What led to this remarkable outcome was the shift to science-led agricultural development, planner’s vigour and the dedicated effort of millions of farmers. This transformed India from an acutely food-scarce and food shortage nation to…
Read More