What is a smart city?
In June 2015, the Prime Minister launched ‘The Smart Cities Mission’ in Bharat, aiming to transform urban areas to make them more citizen-friendly, and sustainable, maintaining hygiene and upgrading to international standards. The mission seeks to harness digital technology to improve the quality of lifts for residents and promote economic growth.
In Bharat, cities accommodate nearly 31% population and 40% in Urban. This mission is an initiative to drive economic growth and improve the quality of life of people by enabling local development and harnessing technology as a means to create smart outcomes for citizens.
Amenities for Smart City
- Adequate Water Supply.
- Assured Electricity Supply.
- Sanitation including solid waste management.
- Affordable housing, especially for the poor.
- Robust IT connectivity and digitalization.
- Good governance, especially e-governance and citizen participation.
- Sustainable environment.
- Safety and security of citizens, particularly women, children, and the elderly
- Heath and education.
Among above water supply system is very important aspects for communities. Till date water supply system is implemented and controlled manually by local administration Gram Panchayat/Municipal Council/ Municipal-Metro Corporation in unorganized way. It has lot of lacuna in uniform water supply, poor water quality control, revenue and lack of operation and maintenance and audit. To overcome those problems, Govt of India has taken initiative and added digital control of water supply as one of important amenities while constructing smart cities. Apart from small cities, ambitious project of AMRUT is also considered for cities not covered under smart city scheme. The said article briefs the digital control water supply system in smart cities
What is digital Control?
Digital describes electronic technology that generates, stores, and processes data in terms of two states: positive and non-positive. Positive is expressed or represented by the number 1 and non-positive by the number 0. Thus, data transmitted or stored with digital technology is expressed as a string of 0’s and 1’s. Each of these state digits is referred to as a bit.
Prior to digital technology, electronic transmission was limited to analogy technology, which conveys data as electronic signals of varying frequency or amplitude that are added to carrier waves of a given frequency. Broadcast and phone transmission have conventionally used analogy technology.
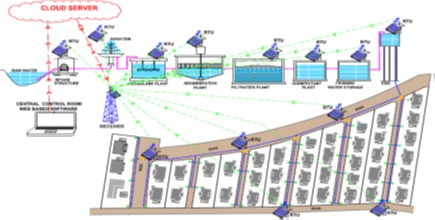
Configuration of Water Supply System
Water Supply System comprises of following components (Fig 1.Configuration of Digital Water Supply System).
- Water Source (River/Lake/Dam).
- Intake Structure (Intake Gallery, Intake Pipe, Motor-pump).
- Aeration.
- Coagulant Plant.
- Sedimentation Plant.
- Filtration Unit.
- Disinfectant Plant.
- Finished Water Storage.
- Elevated Storage Tank (ESR).
- Water Distribution System.
- Digital Control –Automation (IoT Based) – SCADA System.
Philosophy of Digital Control
Philosophy of Digital Based Automation system is based on backward integration of governing parameters like Per capita Demand, Fire demand, Green zone demand, and its judicial use along with price, viability, and assessment of risk. The prime objective of Digital Control is to optimize hassle-free operation, monitoring, management, Billing, Revenue Collections, and on-time service.
Digital automation is comprised of Radio Frequency (RF), Microprocessors, Flow Sensors, Pressure Sensors, Water Level Sensors, EC/pH Control, Water Quality Sensors, Injectors, Electronic Water Meter, Controller, Internet/cell phone connectivity, Laptop/PC, Software for interpreting the information and make the decision to execute the command of various activities in order to provide feedback to users via SMS / What’sapp / Email in a fraction of time.
Various options and combinations of control & operations of input-output are possible on a need basis. Considering the benefits, adaptability, and instant feedback & action facility, the Digital Automation system has great potential as a large-scale water supply system for a city in the world and is successfully implemented in India and abroad at many Municipalities under AMRUT Scheme
AMRUT Scheme.
Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT) was launched in June 2015 by PM under the Government of India. The AMRUT scheme is an initiative to provide basic civic amenities to the urban areas to improve the quality of life with major focus to the poor and the disadvantaged. It is the first focused national water Mission, which was launched in 500 cities and covered 60% of the urban population.
The AMRUT Scheme focuses on establishing an infrastructure for ensuring adequate sewage networks and water supply in the urban areas through the implementation of the urban revival projects. The main objectives of the Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT) are mentioned below:
- To ensure a proper supply of water and a sewage connection in every household.
- To develop green and well-maintained open spaces and parks to increase the amenity value of the cities.
- To reduce pollution by switching to public transport or through the construction of non-motorized transport facilities such as walking and cycling.
- Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT) aims in covering around 500 cities that are having a population of over one lakh with notified municipalities.
- Digital control of water supply Scheme.
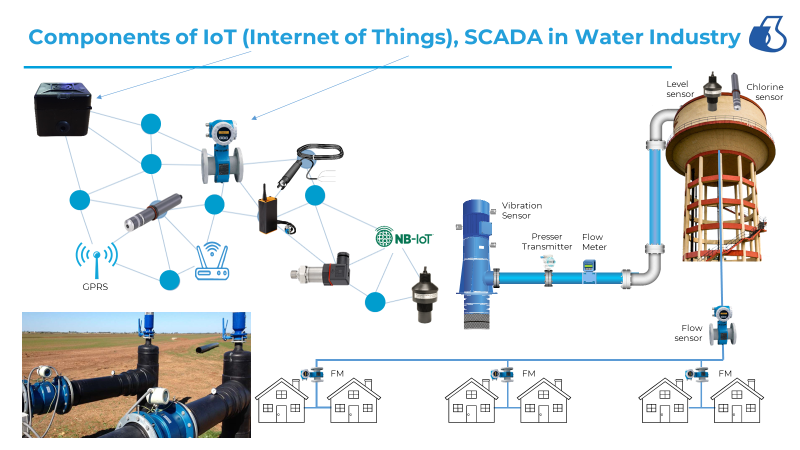
Components of Digital Control
Digital Control System incorporated with hardware and software components for communication of various data from source to end users within a fraction of time very preciously and honestly. The entire data of the project is stored in cloud-based storage and retrieved at any time.
- Hardware.
- Mobile (Android)
- Laptop/PC.
- Digital Water meter.
- RTU (Radio Terminal Unit)
- Controller – microprocessor-based.
- Pressure Sensors.
- Flow Sensors.
- Water level sensors
- EC (Electrical conductivity) & pH Sensors & Monitor.
- Chlorine / Ozone Injector
- Hydraulic valves + pressure pilot + Solenoid
- Weather Station
- Software (Fig 2. Networking)
- Operation & Billing software program.
- Internet network (GSM).
- Cloud Server-Storage
Jain Irrigation Systems Ltd has played a significant role in developing / implementing Digital Control in water supply scheme for City water supply Scheme. In this system, communication among the various equipment/devices is established via electronic media – email or internet, to view the status at glance and accordingly ease to take the decision to optimize utilization of facilities in the right directions – control of timing, uniform distribution of water, water quality control, billing & revenue collections.
The level Digital Control can best be understood and defined by subdividing automation into Six stages.
- Regulating Devices (Control valves, Pressure Regulating valves, Solenoids).
- Measuring Devices (Water meter, flow meters).
- Sensors (EC/Ph sensors, Pressure Sensors, Flow Sensors, Water level sensors).
- Auxiliary Devices (weather station).
- Interpreters/Transmitters/Communicators/Receiver.
- Display, Monitor & Admin + Software (Laptop, mobile, App).
A command is the name given to the mechanism (work to be done) through which a change in status is achieved in field remotely or as per pre-program (eg. On/off command). Commands can be conveyed through a number of media via wi-fi & radio frequency to receptor controller and then finally executed through hydraulically or electrically to get specific result or output. After successful work done acknowledgement message is sent to end users to complete the cycle with preference, predictions, warnings, next turn of work etc.
Following task can be monitored in Digital Control:
- Water Supply by Pre-paid /Post-paid meter to end-users.
- Leak detections in the system.
- Pressure check and regulation.
- Water quality check and control entrances –exist for a cluster network.
- Chemical treatment such as Chlorine / Ozone to cluster network/zone
- Operation of hydraulic valves based on sensors or flow meter/water meter.
- Alarming / warning in case of fault and manual overriding.
- Quantification of water used / demand.
- Trouble shooting in the operation of the system.
- Assessment of risk factors and remedies.
- Record of water volume and accurate billing.
- Optimizing water price to end-user.
- Water conservation.
- Power conservation.
- Assessment of risk factors and mitigation.
- Storage of all data in hard disc and
- Monitoring / Accounting: cost – economics.
- Optimization of the entire process and future planning.
Advantages
- Water conservations
Water can be conserved both by increasing the technical (network) efficiency in the system by introducing leak & fault detections devices, water allocation errors and exploitation of optimum irrigation by interpreting soil moisture, weather data and crop water demand.
- Effective utility of multi water source
Many Water Supply Schemes have more than one water sources located at various distances. Integration of various water sources can be done effectively to minimize the expenses of power and water losses.
- Water Quality Control
Greater efficient dosing of chlorine.
- Energy or Fuel Conservation
Electrical motor pumpsets / Diesel Generator sets can be integrated with Demand-Supply ratio and operation of entire water supply process can be optimized as per need base and thereby consumption of electrical power or fuel cost be optimized.
- Administration cost savings
The abolishment of the need to physically switch on each and every water clock, to manually record each and every flow meter are the main factors that help to reduce the administration costs as well as pinpoint fault location.
- Convenience – The Human factor
It is really impossible to evaluate, quantify and cost & benefits of this factor. In many instance, in addition to wishing to improve the human efficiency, reasons quoted are ‘self- esteem’, Saved persons hours may be quantified but it is harder to evaluate the effect of convenience factor.